Table 16-1
The table below shows the total demand for viewing a rare penguin species at a local reserve. Ecotour companies have to build discreet viewing hides for tourists to view the penguins. Each ecotour company has to pay a fixed fee of $10 000 for the right to build on the reserve. Assume that hides can be supplied to tourists at zero marginal cost. Tickets are sold to tourists to use the viewing hides.
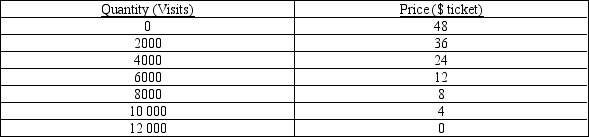 Any firm can change tickets by steps of 1000 only. Prices for missing quantities are the exact midpoint between two adjacent prices.
Any firm can change tickets by steps of 1000 only. Prices for missing quantities are the exact midpoint between two adjacent prices.
-Refer to Table 16-1. Assume that there are two profit-maximising ecotourist companies operating in this market. Further assume that they are able to collude on the price of the tickets they sell. As part of their collusive agreement, they decide to take an equal share of the market. How much profit will each company make?
Definitions:
IPO
Initial Public Offering; the process through which a private company becomes publicly traded by offering its shares for sale to the general public for the first time.
Standby Underwriter
A financial entity that agrees to purchase any unsold shares after a public offering to ensure the issuing company raises the capital needed.
Underpriced IPOs
Initial Public Offerings priced below their market value, often leading to significant investor interest and potential profit.
Q47: A rational pricing strategy for a profit-maximising
Q50: A business-stealing externality is:<br>A) the act of
Q57: Economists who argue that advertising enhances market
Q77: One example of price discrimination occurs in
Q96: The typical firm in the Australian economy
Q98: Which of the following statements are most
Q125: A monopoly can generate a deadweight loss
Q165: When an industry is a natural monopoly:<br>A)
Q166: Monopolistic competition describes a market structure in
Q192: In centrally planned economies the usefulness of