For the following hypothesis test: 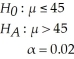 With n = 80,σ = 9,and
With n = 80,σ = 9,and  = 47.1,state the decision rule in terms of the critical value of the test statistic.
= 47.1,state the decision rule in terms of the critical value of the test statistic.
Definitions:
Alzheimer's Disease
A progressive neurological disorder that affects memory, thinking, and behavior, ultimately leading to dementia.
Families
Groups of individuals related by blood, marriage, or a sense of commitment, often forming the basic unit of society.
Beta-Amyloid
A protein fragment snipped from an amyloid precursor protein that, in excessive amounts, can form plaques in the brain and is a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease.
Protein Tau
A protein associated with the stabilization of microtubules in nerve cells, whose abnormal accumulation is linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
Q4: For a standardized normal distribution,determine a value,say
Q10: Under what circumstances would you wish to
Q30: A decision maker wishes to test the
Q36: Suppose the life of a particular brand
Q44: A major shipping company has stated that
Q65: If the population variances are assumed to
Q81: In an effort to estimate the mean
Q87: Suppose nine items are randomly sampled from
Q88: Given a population in which the probability
Q106: The t-distribution is still applicable even when