Given the following null and alternative hypotheses H0 : μ1 ≥ μ2
HA : μ1 < μ2
Together with the following sample information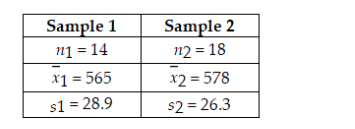 Assuming that the populations are normally distributed with equal variances,test at the 0.05 level of significance whether you would reject the null hypothesis based on the sample information.Use the test statistic approach.
Assuming that the populations are normally distributed with equal variances,test at the 0.05 level of significance whether you would reject the null hypothesis based on the sample information.Use the test statistic approach.
Definitions:
Cognitive Errors
Cognitive errors refer to systematic flaws or biases in human reasoning and perception that can lead to incorrect judgments, decisions, or interpretations.
Counterfactual Thinking
The psychological process of imagining alternative outcomes to events that have already occurred, often starting with "if only" scenarios.
Affective Forecasting
The ability to predict one’s emotional reactions to future events
Psychologists
professionals who study the human mind and behavior, offering insights and interventions for mental and emotional well-being.
Q11: The NCAA is interested in estimating the
Q23: For the following hypothesis: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2693/.jpg" alt="For
Q26: In a two-tailed hypothesis test for the
Q30: A national car rental chain believes that
Q36: A survey was recently conducted in which
Q53: A bank manager wishes to estimate the
Q70: According to data from the Environmental Protection
Q83: If a contingency analysis test is performed
Q124: Explain what is meant by partitioning the
Q147: In hypothesis testing,the null hypothesis should contain