In the production of vitamin capsules,the proportion of calcium in each capsule has a specification of 48 ± 18 parts per million (ppm).An initial random sample of 100 capsules revealed a sample average calcium content of 44.5 ppm and a sample standard deviation of 3.2 ppm.Management uses 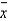
- and R-charts to monitor the calcium amount using samples each of size 4.
The charts depict an in-control process.The center line of the R-chart is 6.7 and the center line of the 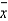
-chart is 44.8.
a.Compute Cp for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard deviation derived from the random sample.
b.Compute Cp for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard deviation derived from the control chart parameters.
c.Compute Cpk for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard deviation derived from the control chart parameters.
c.Compute Cpk for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard deviation derived from the random sample.
d.What do the differences between the values of Cp and Cpk tell you?
Definitions:
External Causes
Factors or circumstances outside of one's control that influence events or outcomes.
Perceivers
Individuals who interpret, process, and assign meaning to information and stimuli they receive from the environment.
Behavior
The behavior or responses of a person in reaction to outside or inside triggers.
Unconscious Attributions
The process of assigning causes to behaviors without conscious awareness, often based on implicit biases or heuristics.
Q3: What is a supplier certification process? What
Q4: Discuss CI tools.
Q10: In which of the following stages of
Q27: Why do organizations focus on improving the
Q29: Which of the following is true regarding
Q35: Which of the following is considered during
Q51: What is the purpose of the Best
Q72: Three scatter diagrams are given below.How many
Q75: The "plan" stage in the PDSA cycle
Q76: In 2002,BSPD received a site visit from