Figure 8-2
The vertical distance between points A and B represents a tax in the market. 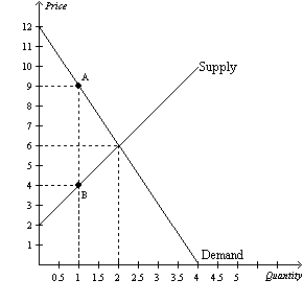
-Refer to Figure 8-2.The imposition of the tax causes the price received by sellers to
Definitions:
Comparative Costs
The analysis or comparison of the costs of different choices or actions to inform decision-making processes.
Activity-Based Costing
A costing method that assigns overhead and indirect costs to specific products or projects based on the activities that drive those costs.
Overhead Allocation
The process of distributing overhead costs, such as rent and utilities, to different departments or products based on a certain criteria or formula.
Cost-Based Pricing
A pricing strategy where the selling price of a product or service is determined by adding a markup to its total cost of production or acquisition.
Q61: Refer to Figure 9-12.With trade allowed,this country<br>A)
Q80: Refer to Figure 7-16.At equilibrium,total surplus is
Q183: Refer to Figure 9-1.With trade,New Zealand will<br>A)
Q202: A tax on raw land causes<br>A) a
Q232: At any quantity,the price given by the
Q240: Refer to Figure 9-18.If Isoland allows international
Q242: Refer to Figure 8-5.The tax causes a
Q247: Suppose that the government imposes a tax
Q308: When a country moves away from a
Q337: Total surplus in a market is consumer