Figure 34-2
(a) The Money Market
(b) The Aggregate Demand Curve 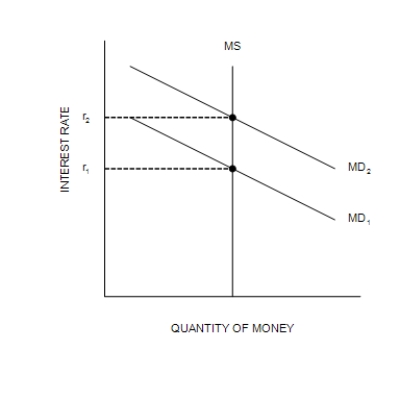
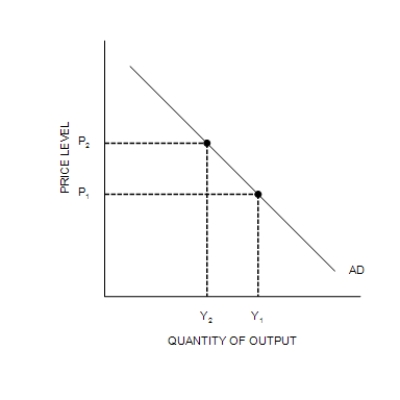
-Refer to Figure 34-2. A decrease in Y from Y1 to Y2 is explained as follows:
Definitions:
Person Schemas
Mental structures that help us organize and interpret information about people, including ourselves and others.
Indigenous Schemas
The conceptual frameworks developed within specific cultures that influence how individuals in those cultures understand and interpret the world around them.
Stereotypes
Preconceived and oversimplified beliefs about certain groups of people that influence behavior and perceptions.
Selective Perception
The process by which individuals selectively interpret what they see based on their interests, background, experience, and attitudes.
Q18: The effects of a higher than expected
Q31: Assuming no crowding-out,investment-accelerator,or multiplier effects,a $100 billion
Q102: Which of the following adjust to bring
Q114: In liquidity preference theory,an increase in the
Q151: Other things the same,an increase in the
Q170: Which of the following is upward sloping?<br>A)
Q176: The short-run Phillips curve indicates that expansionary
Q244: If the long-run Phillips curve shifts to
Q315: If aggregate demand shifts right,then eventually price
Q319: Suppose there are both multiplier and crowding