For m > p2, the demand functions for goods 1 and 2 are given by the equations, 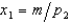 - 1 and
- 1 and 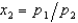 , where m is income and p1 and p2 are prices. Let the horizontal axis represent the quantity of good 1. Let p1 = 1 and p2 = 2. Then for m > 2, the income offer curve is
, where m is income and p1 and p2 are prices. Let the horizontal axis represent the quantity of good 1. Let p1 = 1 and p2 = 2. Then for m > 2, the income offer curve is
Definitions:
Experimenter's Manipulations
The deliberate changes or variations introduced by researchers in an experiment to investigate their effects on the outcome.
Extraneous Variable
Any variable that is not intentionally studied in the experiment which can affect the outcome of the research if not controlled.
Confounding Variable
An outside influence that changes the effect of a dependent and independent variable. This extraneous influence is used to influence the outcome of an experimental design.
Volunteer Bias
A shortcoming of findings derived from a sample of volunteers instead of a representative sample; the volunteers may differ from those who did not volunteer.
Q1: Joseph's utility function is given by U<sub>J</sub>
Q4: If you could exactly afford either 5
Q8: Donald consumes goods x and y. His
Q23: Suppose a consumer is initially endowed with
Q27: Billy Pigskin from your workbook has a
Q27: Nancy Lerner is taking a course from
Q33: A consumer has a utility function given
Q57: The real interest rate is the interest
Q69: Casper's utility function is 3x + y,
Q83: The stability of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6214/.jpg" alt="The stability