The certainty equivalent of a gamble is defined to be the amount of money which, if you were promised it with certainty, would be indifferent to the gamble.
a. If an expected utility maximizer has a von Neuman-Morgenstern utility function U(W) = W 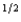
(where W is wealth) and if the probability of events 1 and 2 are both 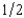 , write a formula for the certainty equivalent of a gamble that gives you x if event 1 happens and y if event 2 happens.
, write a formula for the certainty equivalent of a gamble that gives you x if event 1 happens and y if event 2 happens.
b. Generalize your formula in part (a) to the case where the probability of event 1 is p and the probability of event 2 is 1 - p.
c. Generalize the formula in part (a) to the case where U(W) = Wa for a > 0.
Definitions:
Conditioned Response
is a learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus that occurs because of previous conditioning, typically in the context of classical conditioning.
Unconditioned Stimulus
A stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a reflexive response without the need for prior learning.
Conditioned Stimulus
A previously neutral stimulus that, after being associated with an unconditioned stimulus, elicits a conditioned response in classical conditioning.
Unconditioned Response
An automatic, natural reaction to a stimulus that occurs without prior conditioning or learning.
Q1: Joseph's utility function is given by U<sub>J</sub>
Q7: Pablo's utility function is <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6162/.jpg" alt="Pablo's
Q14: Portia has waited a long time for
Q25: Holly consumes commodities x and y and
Q28: The interest rate is 10% and will
Q36: Oswald Odd consumes only goods 1 and
Q46: Prudence is careful to plan ahead. She
Q75: It is impossible for a person to
Q76: A firm with the production function f
Q88: At the price of $100, tourists demand