A firm uses a single input to produce its output, which is sold in a competitive market. It gets quantity discounts on purchases of its input. If it buys x units of the input, the price it must pay per unit of input is 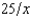 + 4. If it buys no inputs, it doesn't have to pay anything. The firm's production function is f(x) = 60x - x2. If the price of the firm's output is 1, the profit-maximizing amount of input to buy is
+ 4. If it buys no inputs, it doesn't have to pay anything. The firm's production function is f(x) = 60x - x2. If the price of the firm's output is 1, the profit-maximizing amount of input to buy is
Definitions:
Discount
A reduction from the full amount or value of an item or security, often applied to bonds sold below their face value or to promote sales of products.
Coupon Interest Rate
The percentage of a bond's value that is paid out in interest to the bondholder annually, identical to the coupon rate.
Yield To Maturity
The total return anticipated on a bond if it is held until it matures, considering all interest payments and the repayment of principal.
Par Value
The face value or nominal value of a bond, share of stock, or other financial instrument, usually representing its value upon issuance.
Q7: A firm has discovered a new kind
Q12: In a Dutch auction with rational bidders,
Q20: Herb's Auction House in Purloined Hubcap, Oregon,
Q27: An industry has two colluding firms that
Q36: An economy has 2,000 people. 1,000 of
Q38: A profit-maximizing monopolist sets<br>A) price equal to
Q38: In a certain kingdom, the demand function
Q39: A firm has the production function f(x<sub>1</sub>,
Q43: For a monopolist who faces a downward-sloping
Q98: The inverse demand curve P(x) for a