Professor Nightsoils utility function is U N (B N, P N ) = 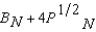 and Dean Interfaces utility function is U I (B I, P I ) =
and Dean Interfaces utility function is U I (B I, P I ) = 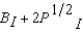 where B N and B I are the number of bromides and P N and P I are the number of platitudes consumed by Nightsoil and Interface respectively. If Nightsoils initial endowment is 4 bromides and 25 platitudes and if Interfaces initial endowment is 2 bromides and 20 platitudes, then at any Pareto efficient allocation in which both consume positive amounts of both goods,
where B N and B I are the number of bromides and P N and P I are the number of platitudes consumed by Nightsoil and Interface respectively. If Nightsoils initial endowment is 4 bromides and 25 platitudes and if Interfaces initial endowment is 2 bromides and 20 platitudes, then at any Pareto efficient allocation in which both consume positive amounts of both goods,
Definitions:
MBCA
Model Business Corporation Act, a recommendation for state law on corporations, providing a template for corporate governance and operations.
Net Asset Test
A financial assessment to determine a company's or individual's net worth by subtracting total liabilities from total assets.
Revised Act
Refers to legislation that has been updated or amended to incorporate changes or new provisions since its original enactment.
Earned Surplus
Profits that a company has retained rather than distributed to shareholders, typically used for reinvestment in the business or to pay down debt.
Q2: A general has the two possible pure
Q10: In Problem 9, Billy has a von
Q10: Which of the following is the best
Q11: If the number of persons who attend
Q14: Mr. Cog in Problem 7 has 18
Q14: In Problem 7, Harry Mazzola has the
Q24: In the Cournot model, each firm chooses
Q25: In Problem 1, if Abishag owned 6
Q42: Marbella has 101 residents. All wear the
Q49: An industry has 100 firms. These