In Problem 2, Ambrose has the utility function U(x1, x2) 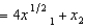 . If Ambrose were initially consuming 81 units of nuts (good 1) and 22 units of berries (good 2) , then what is the largest number of berries that he would be willing to give up in return for an additional 40 units of nuts?
. If Ambrose were initially consuming 81 units of nuts (good 1) and 22 units of berries (good 2) , then what is the largest number of berries that he would be willing to give up in return for an additional 40 units of nuts?
Definitions:
Framing Effect
A cognitive bias where people react differently to a choice depending on how it is presented, or "framed," especially as a loss or gain.
Belief Perseverance
The psychological phenomenon where individuals maintain their convictions even when confronted with contrary evidence, showcasing the difficulty of changing deeply held beliefs.
Framing Effect
The cognitive bias where people's decisions are influenced by the way information is presented, rather than just the information itself.
Representativeness Heuristic
A cognitive shortcut that involves making judgments based on how well something matches or represents a particular prototype.
Q6: A substantial majority of Americans have inadequate
Q9: In Problem 1, Charlie's indifference curves have
Q10: People find it easier to commit to
Q12: If the number of persons who attend
Q13: In Problem 1, Charlie's indifference curves have
Q15: In a pure exchange economy if the
Q23: There are two major producers of corncob
Q23: A firm uses 3 factors of production.
Q25: This problem will be easier if you
Q39: Mike's utility function is U(c, d, h)