(See Problem 11.) Pete's expected utility function is 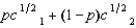 , where p is the probability that he consumes c1 and 1 - p is the probability that he consumes c2. Pete is offered a choice between getting a sure payment of $Z or a lottery in which he receives $1,600 with probability .80 or $14,400 with probability .20. Pete will choose the sure payment if
, where p is the probability that he consumes c1 and 1 - p is the probability that he consumes c2. Pete is offered a choice between getting a sure payment of $Z or a lottery in which he receives $1,600 with probability .80 or $14,400 with probability .20. Pete will choose the sure payment if
Definitions:
Allocation
The process of distributing resources, goods, or services in a particular way or to particular recipients.
Scarce Resources
Resources that are limited in supply and cannot fulfill all the uses and demands placed on them.
Virtually Unlimited
A term used to describe a resource or supply that is so abundant it appears to be almost without limit.
Scarcity and Choice
Refers to the fundamental economic problem of having unlimited human wants in a world of limited resources, leading to the necessity of making choices on how to allocate resources efficiently.
Q7: In Problem 2, the production function is
Q9: Hatfield and McCoy burn with hatred for
Q10: Charlie's utility function is U(x<sub>A</sub>, x<sub>B</sub>) =
Q12: Two stores are located side by side
Q14: In Problem 2, suppose that a new
Q15: In Problem 9, suppose that Irma's production
Q18: In Problem 3, the production function is
Q21: If Peregrine in Problem 1 consumes (1,
Q23: In Problem 5, the demand function for
Q26: Hatfield and McCoy burn with hatred for