(See Problem 11.) Pete's expected utility function is 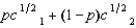 , where p is the probability that he consumes c1 and 1 - p is the probability that he consumes c2. Pete is offered a choice between getting a sure payment of $Z or a lottery in which he receives $1,600 with probability .80 or $14,400 with probability .20. Pete will choose the sure payment if
, where p is the probability that he consumes c1 and 1 - p is the probability that he consumes c2. Pete is offered a choice between getting a sure payment of $Z or a lottery in which he receives $1,600 with probability .80 or $14,400 with probability .20. Pete will choose the sure payment if
Definitions:
Shareholder Scrutiny
The analysis and evaluation of a company's performance and governance by its shareholders, often to assess the effectiveness, policies, and strategic direction of management.
Terminal Growth Rate
The rate at which a company is expected to grow its dividends or free cash flow beyond the forecast period, into perpetuity, during valuation.
Multi Stage Growth Model
A valuation method that applies different rates of growth to a company's earnings or dividends over various time horizons.
Discount Rate
The interest rate used to determine the present value of future cash flows.
Q3: A group of 13 consumers are trying
Q5: Suppose that in Problem 2, the demand
Q8: In Problem 11, ads in the boring
Q9: Chillingsworth from Problem 10 has a neighbor,
Q15: In Problem 6, Elmer's utility function is
Q16: Mike's utility function is U(c, d, h)
Q22: If the demand curve for the DoorKnobs
Q27: Chillingsworth from Problem 10 has a neighbor,
Q29: Suppose that low-productivity workers all have marginal
Q41: Suppose that in Horsehead, Massachusetts, the cost