In Problem 3, Professor Nightsoil's utility function is UN(BN, PN) 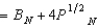 and Dean Interface's utility function is UI(BI, PI)
and Dean Interface's utility function is UI(BI, PI) 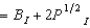 . If Nightsoil's initial endowment is 6 bromides and 20 platitudes and if Interface's initial endowment is 2 bromides and 10 platitudes, then at any Pareto efficient allocation where both persons consume positive amounts of both goods,
. If Nightsoil's initial endowment is 6 bromides and 20 platitudes and if Interface's initial endowment is 2 bromides and 10 platitudes, then at any Pareto efficient allocation where both persons consume positive amounts of both goods,
Definitions:
Defense of Marriage Act
A now-defunct U.S. federal law enacted in 1996 that defined marriage as the union between one man and one woman for federal and inter-state recognition purposes, before being ruled unconstitutional.
Gay Marriage
The legally or socially recognized marriage between two individuals of the same sex.
Peer Delinquent Subculture
A group of peers with norms and values that deviate from mainstream society's, often engaging in anti-social or criminal behavior.
Brothel Sex Worker
An individual who provides sexual services for money within a brothel, a place specifically dedicated to prostitution.
Q1: A firm has invented a new beverage
Q3: Suppose that the garden gnome industry was
Q4: In Problem 8, if a = 2.40,
Q12: Suppose that the garden gnome industry was
Q13: Recall Bonnie and Clyde from Problem 5.
Q25: (See Problem 6.) Big Pig and Little
Q51: Discuss what it means for a futures
Q102: Would you be willing to exchange dollars
Q102: Which one of the following characteristics is
Q104: If prices in the United States rise