In Problem 2, suppose that the cost function of the honey farm is CH(H, A) = 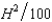 - 3A and the cost function of the apple orchard is CA(H, A) =
- 3A and the cost function of the apple orchard is CA(H, A) = 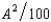 , where H and A are the number of units of honey and apples produced respectively. The price of honey is $7 and the price of apples is $5 per unit. Let A1 be the output of apples if the firms operate independently, and let A2 be the output of apples if the firms are operated by a profit-maximizing single owner.
, where H and A are the number of units of honey and apples produced respectively. The price of honey is $7 and the price of apples is $5 per unit. Let A1 be the output of apples if the firms operate independently, and let A2 be the output of apples if the firms are operated by a profit-maximizing single owner.
Definitions:
Epidermis
The outer layer of cells covering an organism, particularly the surface epithelium of the skin of animals.
Stratum
A layer or level within a hierarchical structure, such as the layers of the skin or atmosphere.
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost layer of skin, providing a waterproof barrier and creating our skin tone.
Stratum
A layer or level in an organized structure, such as in the skin or social hierarchy.
Q1: In a crowded city far away, the
Q4: If the demand function for the DoorKnobs
Q13: In Problem 9, suppose that Irma's production
Q17: Jennifer sold a call option on XXX
Q22: In Problem 5, the demand function for
Q26: You're hoarse from explaining to your supervisor
Q43: A large dental lab plans to purchase
Q58: How do we perform an NPV analysis
Q75: How much must the stock be worth
Q118: Generalize the formulas for determining the value