Moss Manufacturing has just completed a major change in its quality control (QC) process. Previously, products had been reviewed by QC inspectors at the end of each major process, and the company's ten QC inspectors were charged as direct labor to the operation or job. In an effort to improve efficiency and quality, a computerized video QC system was purchased for $250,000. The system consists of a minicomputer, 15 video cameras, other peripheral hardware, and software.
The new system used cameras stationed by QC engineers at key points in the production process. Each time an operation changes or there is a new operation, the cameras are moved, and a new master picture is loaded into the computer by a QC engineer. The camera takes pictures of the units in process, and the computer compares them to the picture of a "good" unit. Any differences are sent to a QC engineer who removes the bad units and discusses the flaws with the production supervisors. The new system has replaced the ten QC inspectors with two QC engineers.
The operating costs of the new QC system, including the salaries of the QC engineers, have been included as factory overhead in calculating the company's volume-based factory overhead rate which is based on direct labor dollars.
The company's president is confused. His vice president of production has told him how efficient the new system is, yet there is a large increase in the factory overhead rate. The computation of the rate before and after automation is shown below. 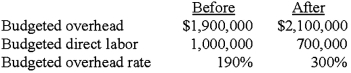 "Three hundred percent," lamented the president, "How can we compete with such a high factory overhead rate?"
"Three hundred percent," lamented the president, "How can we compete with such a high factory overhead rate?"
Required:
1. a. Define factory overhead, and cite three examples of typical costs that would be included in factory overhead.
b. Explain why companies develop factory overhead rates.
2. Explain why the increase in the overhead rate should not have a negative financial impact on Moss Manufacturing.
3. Explain, in the greatest detail possible, how Moss Manufacturing could change its overhead accounting system to eliminate confusion over product costs.
Definitions:
Control Accounts
Accounts used in the general ledger to summarize the detail contained in a subsidiary ledger, helping to simplify and organize financial information.
Factory Labor
The workforce engaged in operating machinery and performing tasks involved in the manufacturing process.
Factory Wages Payable
Liabilities accounts that represent amounts owed to factory workers for wages earned but not yet paid.
Subsidiary Ledger
A Subsidiary Ledger is a ledger containing all details of transactions for a specific account, which then summarizes into a single line in the General Ledger.
Q9: The story of the telecom giant WorldCom
Q14: When a firm is determining its opportunities
Q18: The objective of the fourth step in
Q28: When participants are not aware of whether
Q61: Phillipe, a researcher, examined the effect of
Q70: Using activity-based costing, applied machinery overhead for
Q80: Which of the following is not a
Q95: Extending the length of a time period
Q104: A retailer, in business for over 50
Q108: Which of the four types of cost