Figure 21.2 shows the benefit functions for low-ability workers and high-ability workers (A and B) ,along with one indifference curve for each worker type (C and D) .The employer cannot observe worker type directly but has created two positions,E and F,as a screening mechanism.Which of the following is true? 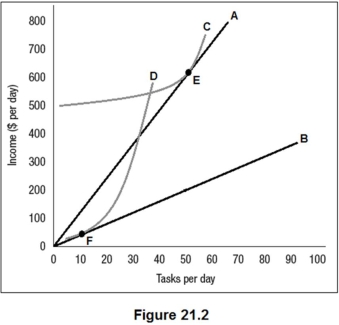
Definitions:
Debit Card
A payment card that deducts money directly from a consumer’s checking account to pay for a purchase.
Traveler's Check
A preprinted, fixed-amount check designed to allow the person signing it to exchange it for cash in a foreign currency while traveling.
Conference Expenses
Costs associated with attending or hosting a professional gathering, including travel, accommodation, and registration fees.
Forwarding Address
An address where mail is sent after the recipient has moved from their previous location, ensuring the mail reaches the correct party.
Q8: The plaintiff's burden of proof in a
Q11: How do courts deal with the situation
Q13: The prohibition against excessive bail and fines
Q19: Suppose milk and cereal are compliments and
Q39: Jim and Slater want to buy a
Q43: Suppose Always There Wireless serves 100 high-demand
Q49: The _ consumers make decisions about whether
Q54: The market demand function for wheat is
Q56: The value of a worker's marginal product
Q60: In a market for homogenous goods:<br>A) firms