Six Sigma is one approach for setting quality expectations for a given process or output. As pointed out in Chapter 17 of your text, the term "Six Sigma" comes from statistics: in a normal distribution, the area (probability) outside of +/− six (6) standard deviations from the mean value is exceedingly small. You are provided the following values from a standardized normal distribution (i.e., a distribution with a mean of zero and a standard deviation of 1.0): Note: The Z values in the above table refer to the number of sigmas to the right of center (i.e., to the right of Z = 0). The listed probabilities, p, refer to the area to the right of the chosen Z point, as illustrated by the graph below: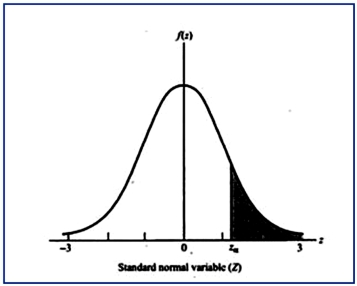 Required:
Required:
1. Given the above, what is the total probability (area under the curve) corresponding to Z = 0 +/− 1.0 sigma, rounded to two decimal places (e.g., 0.34817 = 34.82%)? How many units (out of 1,000 outputs) would have one or more defects for a process operating at one-sigma performance level? Round your answer to nearest whole number.
2. What is the total probability (area under the curve) corresponding to Z = 0 +/− 3.0 sigma, rounded to two decimal places? How many units (out of 1,000 outputs) would have one or more defects for a process operating at three-sigma performance level? Round your answer to nearest whole number.
3. Under a four-sigma control level, what is the total area in the two tails of the distribution, rounded to six (6) decimal places (e.g., 0.00004169 = 0.00417%). What is the total probability (area under the curve) corresponding to Z = 0 +/− 4.0 sigma, rounded to two decimal places? How many units (out of 100,000 outputs) would have one or more defects for a process operating at four-sigma performance level? Round your answer to nearest whole number.
4. What general conclusion can you draw based on the preceding results?
Definitions:
Trial Balance
A trial balance is a bookkeeping worksheet in which the balances of all ledgers are compiled into debit and credit account column totals that are equal.
Slide
An error in accounting that occurs when a number is incorrectly transferred from one document to another, missing or adding a digit.
Error
A mistake or discrepancy in documents or calculations, often requiring correction or adjustment.
Trial Balance
A ledger summary sheet where the sums of all accounts are organized into equal columns for both debits and credits.
Q55: Which of the following statements regarding the
Q56: If the organization is making good progress
Q64: The evaluation of operating level employees by
Q70: Under full costing, fixed manufacturing overhead costs
Q101: Selected data from Chering Division's accounting
Q104: The market size variance arises because of
Q105: A total variable cost variance (such as
Q138: Which of the following items would most
Q156: Ben Simon Corp. has the following information
Q171: The primary purpose of calculating standard cost