Six Sigma is one approach for setting quality expectations for a given process or output. As pointed out in Chapter 17 of your text, the term "Six Sigma" comes from statistics: in a normal distribution, the area (probability) outside of +/− six (6) standard deviations from the mean value is exceedingly small. You are provided the following values from a standardized normal distribution (i.e., a distribution with a mean of zero and a standard deviation of 1.0): Note: The Z values in the above table refer to the number of sigmas to the right of center (i.e., to the right of Z = 0). The listed probabilities, p, refer to the area to the right of the chosen Z point, as illustrated by the graph below: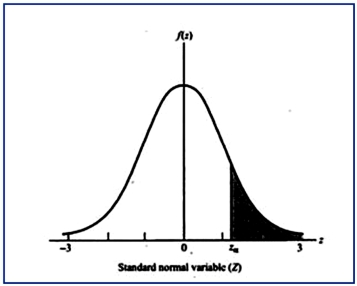 Required:
Required:
1. Given the above, what is the total probability (area under the curve) corresponding to Z = 0 +/− 1.0 sigma, rounded to two decimal places (e.g., 0.34817 = 34.82%)? How many units (out of 1,000 outputs) would have one or more defects for a process operating at one-sigma performance level? Round your answer to nearest whole number.
2. What is the total probability (area under the curve) corresponding to Z = 0 +/− 3.0 sigma, rounded to two decimal places? How many units (out of 1,000 outputs) would have one or more defects for a process operating at three-sigma performance level? Round your answer to nearest whole number.
3. Under a four-sigma control level, what is the total area in the two tails of the distribution, rounded to six (6) decimal places (e.g., 0.00004169 = 0.00417%). What is the total probability (area under the curve) corresponding to Z = 0 +/− 4.0 sigma, rounded to two decimal places? How many units (out of 100,000 outputs) would have one or more defects for a process operating at four-sigma performance level? Round your answer to nearest whole number.
4. What general conclusion can you draw based on the preceding results?
Definitions:
Empirically Based Practice
Empirically based practice involves using strategies and methods that have been proven effective through empirical research and systematic observation in professional fields.
Scientific Evidence
Information, facts, or data that are systematically observed, recorded, and tested through scientific methods to establish facts or principles.
Client System
The group of people or entities that are the focus of professional intervention or service efforts.
Pincus and Minahan
Refers to Allan Pincus and Anne Minahan, who are known for their contributions to the field of social work, particularly in the development of the systems theory framework.
Q6: Machine Builders Inc. adopted a standard cost
Q15: An organization's overall management accounting and control
Q88: Which of the following are computer-based databases
Q88: Efforts to improve productivity should be focused
Q97: Which of the following would explain why
Q97: Nappon Co. has two products named
Q111: Winston Co. had two products code
Q129: In the principal-agent model, the manager is
Q132: Studies have shown that improvements in quality
Q153: The difference in each period between total