(Originally "Problem Eleven" from Chapter Six in previous editions of the textbook)
Alpha Ltd.is a Canadian-controlled private corporation operating a small land-development business.In June 20X2,it acquired a license to manufacture pre-fab homes and began operations immediately.Financial information for the 20X2 taxation year is outlined below:
Alpha's profit before income taxes for the year ended November 30,20X2,was $245,000,as follows: 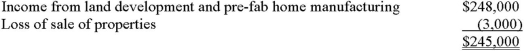 The loss on sale of property results from two transactions.On October 1,20X2,Alpha sold all of its shares of Q Ltd.,a 100% subsidiary,for $100,000.(The shares were acquired seven years ago for $80,000.)Also,during the year,Alpha sold some of its vehicles for $25,000.The vehicles originally cost $50,000 and had a book value of $48,000 at the time of sale.New vehicles were obtained under a lease arrangement.
The loss on sale of property results from two transactions.On October 1,20X2,Alpha sold all of its shares of Q Ltd.,a 100% subsidiary,for $100,000.(The shares were acquired seven years ago for $80,000.)Also,during the year,Alpha sold some of its vehicles for $25,000.The vehicles originally cost $50,000 and had a book value of $48,000 at the time of sale.New vehicles were obtained under a lease arrangement.
The 20X1 corporate tax return shows the following UCC balances:  Alpha occupies leased premises under a seven-year lease agreement that began three years ago.At the time,Alpha spent $60,000 to improve the premises.The lease agreement gives Alpha the option to renew the lease for two three-year periods.Alpha began manufacturing pre-fab homes on June 1,20X2.At that time,it acquired the following:
Alpha occupies leased premises under a seven-year lease agreement that began three years ago.At the time,Alpha spent $60,000 to improve the premises.The lease agreement gives Alpha the option to renew the lease for two three-year periods.Alpha began manufacturing pre-fab homes on June 1,20X2.At that time,it acquired the following: 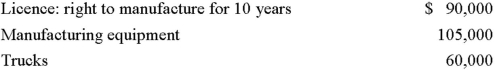 Accounting amortization in 20X2 amounted to $60,000.
Accounting amortization in 20X2 amounted to $60,000.
Alpha normally acquires raw land,which it then develops into building lots for resale to individuals or housing contractors.In 20X2,it sold part of its undeveloped land inventory to another developer for $400,000.The sale realized a profit of $80,000,which is included in the land-development income above.The proceeds consisted of $40,000 in cash,with the balance payable in five annual instalments beginning in 20X3.
Travel and entertainment expense includes the following:  Legal and accounting expense includes the following:
Legal and accounting expense includes the following:  Required:
Required:
Calculate Alpha's net income for tax purposes for the 20X2 taxation year.
Definitions:
Short-Run Equilibrium
A state in which supply equals demand within a particular market, specifically under the assumption that some conditions (like input prices) are fixed in the short term.
Marginal Cost
The charge for the production of one more unit of a product or service.
Marginal Revenue
The enhanced earnings a firm receives from offloading an extra unit of a good or service.
Marginal Cost
Marginal cost is the increase in total cost that arises from producing one additional unit of a good or service, a critical concept in economic decision-making and pricing strategies.
Q2: Allison Hill moved to Canada on April
Q4: Which of the following statements regarding recapture
Q7: What is customer share? How can a
Q7: Car Co.is selling its land and building
Q16: The World Resources Institute has defined:<br>A)Types of
Q30: The emphasis on effective _ has _
Q48: Salespeople are often told to "work smarter,not
Q50: Which one of the following customer critical
Q56: Career and sales goals should be challenging
Q67: Salespeople should develop relationships with manufacturing so