Scenario 9-2
• For a small country called Boxland,the equation of the domestic demand curve for
cardboard is  ,
,
where 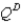 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded,in tons,and
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded,in tons,and 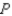 represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
• For Boxland,the equation of the domestic supply curve for cardboard is 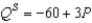 ,
,
where 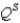 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied,in tons,and
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied,in tons,and 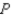 again
again
represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
-Refer to Scenario 9-2.Suppose the world price of cardboard is $45.Then,relative to the no-trade situation,international trade in cardboard
Definitions:
Economic Efficiency
A condition where resources are allocated in a way that maximizes the production of goods and services without wasting any resources.
Economic Efficiency
occurs when resources are allocated in a way that maximizes the production of goods and services at the lowest cost, minimizing waste and inefficiency.
Automobile Safety
Automobile Safety involves the design, equipment, and regulations that aim to minimize the occurrence and consequences of traffic accidents.
Additional Cost
Expenses that are not initially planned for but arise during the production or execution of a project, also known as incidental or unforeseen costs.
Q52: Refer to Figure 8-15. Panel (a) and
Q138: Refer to Figure 8-18. Suppose the government
Q171: "Owners of firms in young industries should
Q255: Refer to Figure 10-9. Which graph represents
Q256: Some goods can be produced at low
Q292: Refer to Figure 9-15. With trade and
Q314: The goal of industrial policy should be
Q375: Refer to Figure 9-29. Suppose the country
Q477: For any country, if the world price
Q511: Refer to Scenario 10-1. Let Q represent