A monopolist faces the following demand curve: 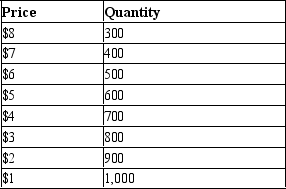 The monopolist has fixed costs of $1,000 and has a constant marginal cost of $2 per unit. If the monopolist were able to perfectly price discriminate, how many units would it sell?
The monopolist has fixed costs of $1,000 and has a constant marginal cost of $2 per unit. If the monopolist were able to perfectly price discriminate, how many units would it sell?
Definitions:
Fixed Costs
Costs that do not change in total despite fluctuations in the volume of goods or services produced or sold.
Variable Costs
Charges that fluctuate according to the degree of business operations.
Cost-volume-profit Graph
A graphical representation that shows the relationship between a company's costs, its sales volume, and its profits, used for planning and decision-making.
CVP Graph
A visual representation of the Cost-Volume-Profit analysis, illustrating the relationship between costs (both variable and fixed), volume of production, and the resulting profit or loss.
Q35: Long-run profit earned by a monopolistically competitive
Q39: Consider monopoly, monopolistic competition, and perfect competition.
Q165: When a market is monopolistically competitive, the
Q175: Refer to Scenario 15-11. Vincent uses a
Q194: Refer to Table 15-12. If the firm
Q299: Refer to Figure 16-2. If the average
Q468: The DeBeers Company faces very little competition
Q484: The monopolist's profit-maximizing quantity of output is
Q494: Refer to Figure 15-13. A profit-maximizing monopolist
Q631: Refer to Scenario 15-3. At Q =