Table 17-5
The information in the table below shows the total demand for premium-channel digital cable TV subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each digital cable TV operator pays a fixed cost of $200,000 (per year) to provide premium digital channels in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the premium channel service to a household is zero. 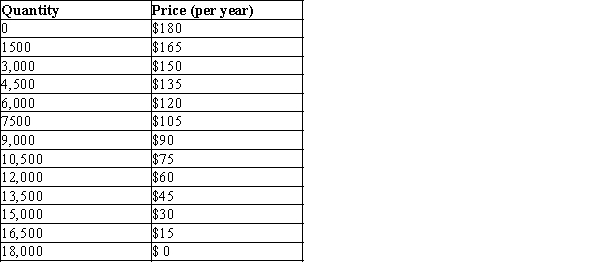
-Refer to Table 17-5. Assume there are two profit-maximizing digital cable TV companies operating in this market. Further assume that they are not able to collude on the price and quantity of premium digital channel subscriptions to sell. How many premium digital channel cable TV subscriptions will be sold altogether when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium?
Definitions:
Indifference Curves
Graphical representations used in microeconomics to show different combinations of two goods that give a consumer equal satisfaction and utility.
Marginal Rate
Marginal Rate often refers to the additional cost or benefit associated with a slight increase in production or activity, influencing decisions in finance and economics.
Convex
A shape or function where a line segment between any two points on its boundary or graph lies above or on the shape or graph.
Transitivity
In decision theory, the principle that if a person prefers option A to B and B to C, then they should prefer A to C.
Q11: Refer to Table 16-5. What is this
Q14: Total income in the United States is
Q32: . What happens when the prisoners' dilemma
Q56: In which of the following market structures
Q80: The prisoners' dilemma game<br>A) is a situation
Q139: How did the Clayton Act of 1914
Q265: Refer to Table 17-11. ABC and XYZ
Q405: Refer to Figure 16-12. How much excess
Q433: If the output effect from increased production
Q479: Refer to Figure 16-10. In order to