Figure 21-32 The figure shows three indifference curves and a budget constraint for a consumer named Hannah. When young, Hannah works and earns income. When old, she is retired and earns no income. 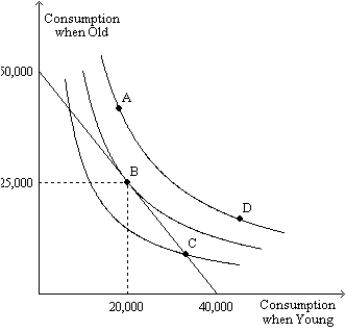
-Refer to Figure 21-32. From the figure we can determine how much income Hannah earns when young and we can determine the interest rate. Could the interest rate rise to a level at which Hannah could afford to be at point A?
Definitions:
P(A and B)
The probability of both event A and event B occurring in a combined manner.
P(A or B)
The probability of event A happening, event B happening, or both events happening.
P(A)
Denotes the probability of event A happening.
P(B)
The probability notation referring to the likelihood of event B occurring.
Q34: Refer to Table 22-21. What is the
Q76: Suppose that you have $100 today and
Q164: Refer to Figure 21-17. When the price
Q168: Two economists found empirical evidence that when
Q187: Insurance companies charge annual premiums to collect
Q192: In a vote between options A, B,
Q283: Refer to Figure 21-1. All of the
Q330: The Condorcet paradox<br>A) proved that the Arrow
Q371: Refer to Scenario 22-6. What is the
Q432: When Matt has an income of $2,000,