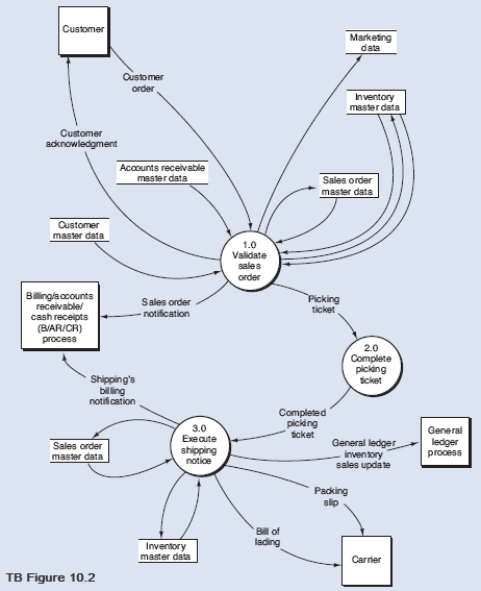
Below is a narrative of the "Validate sales order" portion (i.e., bubble 1.0) of the order entry/sales process.
Narrative Description
How does the OE/S process then validate a customer order? First, process 1.1 verifies the availability of the requested inventory by consulting the inventory master data. If a sufficient level of inventory is on hand to satisfy the request, the order is forwarded for further processing, as depicted by the data flow "Inventory available order." Conversely, if a customer orders goods that are not in stock, process 1.1 runs a special back order routine. This routine determines the inventory requirement necessary to satisfy the order and then sends the back order request to the purchasing department. This activity is depicted by the "Back order" data flow, which in reality is a specific type of exception routine (i.e., a specific type of reject stub). If the customer refuses to accept a back order, then the sales event is terminated and the order is rejected, as shown by the "Reject" data flow. Information from the order (e.g., sales region, customer demographics, and order characteristics that reflect buying habits) that has potential value to marketing is recorded in the marketing data store.
After assuring inventory availability, process 1.2 establishes the customer's existence and then evaluates credit. The credit check adds the amount of the order to accounts receivable balances and open sales orders (i.e., orders about to be receivables), and compare that total to the credit limit. If the customer has exceeded their credit limit, the order is rejected.
Upon a successful credit approval, process 1.3 performs the following activities simultaneously:
.
.
Required:
From the DFD in TB Figure 10.2 and the narrative description above, explode bubble 1.0 into a lower-level diagram showing the details of that process.
Definitions:
Ranking Conflicts
Disputes arising from the prioritization or ordering of different interests, claims, or benefits.
Mutually Exclusive
A term used to describe situations, events, or decisions where the occurrence of one precludes the occurrence of the others.
Independent
A term describing events that are not affected by other events, or variables with no association or influence on each other.
Net Present Value
A calculation that compares the value of all cash inflows and outflows of a project or investment using a specified discount rate.
Q3: Which of the following documents represents a
Q25: The concept behind _ is to cultivate
Q31: In a logical DFD for a B/AR/CR
Q43: The cashier usually reports to the _.
Q62: The inventory master data contains a record
Q63: IT governance is a process that ensures
Q66: Preformatted screens in the OE/S process are
Q68: Below is the narrative of the "Manage
Q100: Inputs to the B/AR/CR process normally could
Q123: Organizations should reconcile their _ on a