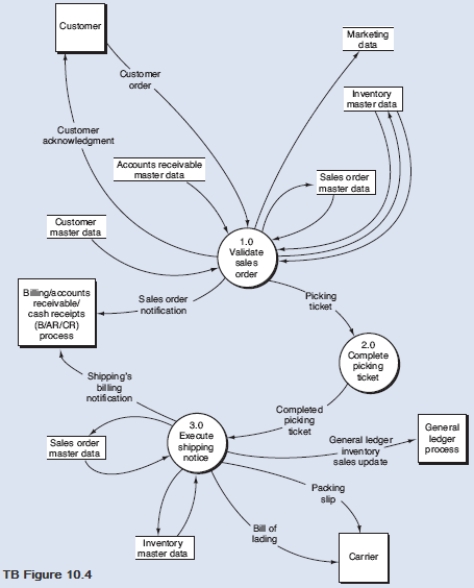
Below is a narrative of the "Validate sales order" portion (i.e., bubble 1.0) of the order entry/sales process.
Narrative Description
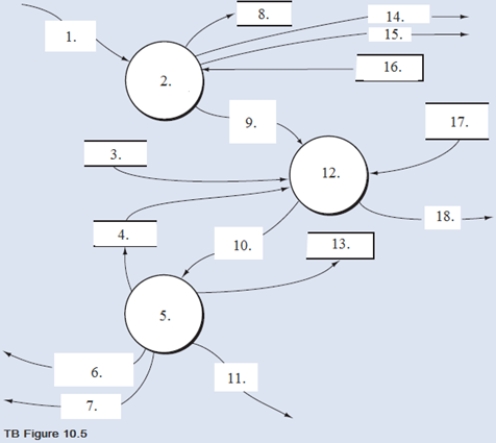
How does the OE/S process then validate a customer order? First, process 1.1 verifies the availability of the requested inventory by consulting the inventory master data. If a sufficient level of inventory is on hand to satisfy the request, the order is forwarded for further processing, as depicted by the data flow "Inventory available order." Conversely, if a customer orders goods that are not in stock, process 1.1 runs a special back order routine. This routine determines the inventory requirement necessary to satisfy the order and then sends the back order request to the purchasing department. This activity is depicted by the "Back order" data flow, which in reality is a specific type of exception routine (i.e., a specific type of reject stub). If the customer refuses to accept a back order, then the sales event is terminated and the order is rejected, as shown by the "Reject" data flow. Information from the order (e.g., sales region, customer demographics, and order characteristics that reflect buying habits) that has potential value to marketing is recorded in the marketing data store.
After assuring inventory availability, process 1.2 establishes the customer's existence and then evaluates credit. The credit check adds the amount of the order to accounts receivable balances and open sales orders (i.e., orders about to be receivables), and compare that total to the credit limit. If the customer has exceeded their credit limit, the order is rejected.
Upon a successful credit approval, process 1.3 performs the following activities simultaneously:
Required:
From the DFD in TB Figure 10.4 and the narrative description above, explode bubble 1.0 into a lower-level diagram showing the details of that process by identifying the words that belong in items 1 to 18 (TB Figure 10.5).
Definitions:
Triassic
A geological period that occurred approximately 252 to 201 million years ago, marking the beginning of the Mesozoic Era.
Cretaceous
The last period of the Mesozoic Era, marked by significant geological events and the extinction of dinosaurs.
Pleistocene
The geological epoch from about 2.6 million to 11,700 years ago, characterized by the last ice ages and the emergence of Homo sapiens.
Carboniferous
A geologic period and system that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period 358.9 million years ago, to the beginning of the Permian Period.
Q16: The section of Sarbanes Oxley that makes
Q17: The manager of shipping reviews a file
Q23: _ segregates duties between the personnel who
Q32: A control that can ensure that receiving
Q48: _ control the online entry of data
Q52: In selecting a vendor, a buyer may
Q53: As used in the purchasing process chapter,
Q64: _ may reduce input errors by populating
Q91: In an online environment, _ ensures that
Q99: A credit card system is better at