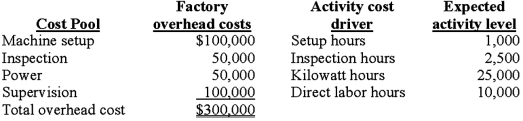
Demski Company has used a two-stage cost allocation system for many years. In the first stage, plant overhead costs are allocated to two production departments, P1 and P2, based on machine hours. In the second stage, Demski uses direct labor hours to assign overhead costs from the production departments to individual products A andB.
Budgeted factory overhead costs for the year are $300,000. Both the budgeted and actual machine hours in P1 and P2 are 12,000 and 28,000 hours, respectively.
After attending a seminar to learn the potential benefits of adopting an activity-based costing system (ABC), Ted Demski, the president of Demski Company, is considering implementing an ABC system. Upon his request, the controller at Demski Company has compiled the following information for analysis:
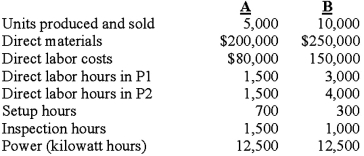
 Demski manufactures two types of product, A and B, for which the following information is available:
Demski manufactures two types of product, A and B, for which the following information is available:
 Required:
Required:
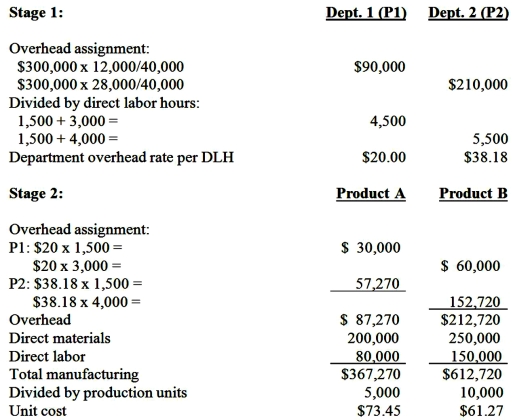
1. Determine the unit cost for each of the two products using the traditional two-stage allocation method. Round calculations to 2 decimal places.
2. Determine the unit cost for each of the two products using the proposed ABC system.
3. Compare the unit manufacturing costs for product A and product B computed in requirements 1 and 2.
(a) Why do two the cost systems differ in their total cost for each product?
(b) Why might these differences be important to the Demski Company?
Answer may vary
Feedback: 1. Unit cost for each of two products using the traditional two-stage allocation method:
Definitions:
Intermediate Filament
Stable cytoskeletal element of animals and some protists; structurally supports cell membranes and tissues; also forms external structures such as hair.
Cytoskeletal Element
Component of the cytoskeleton, providing structure and shape to cells, and involved in cell division, movement, and transport of materials within the cell.
Centriole
In animal cells, a barrel-shaped organelle from which microtubules grow.
Cilia
Microscopic, hair-like structures on the surface of certain cells that move in a wave-like manner, facilitating movement or the transport of fluids and particles.
Q9: Cost of goods manufactured is calculated to
Q17: Cost allocation of shared facilities cost is
Q25: If Orange, Inc. uses machine hours to
Q45: Abnormal spoilage is considered what kind of
Q48: The total cost of Job X is:<br>A)$152,400.<br>B)$128,200.<br>C)$151,900.<br>D)$129,600.<br>E)$140,800.
Q50: The percentage of completion of the beginning
Q50: General corporate sales expenditures are:<br>A)Customer unit-level costs.<br>B)Customer
Q58: Andrews & Henderson Inc. is a manufacturer
Q59: Manufacturers of large equipment such as aircraft
Q96: If Activity X had a budgeted cost