Figure 2.5 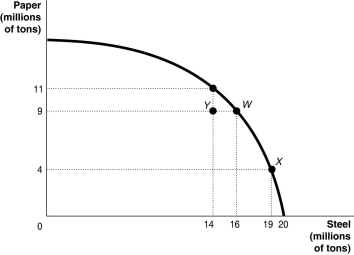 Alt text for Figure 2.5: In figure 2.5, a graph compares paper and steel production.
Alt text for Figure 2.5: In figure 2.5, a graph compares paper and steel production.
Long description for Figure 2.5: The x-axis is labelled, steel in millions of tons and the quantities 14, 16, 19, and 20 are marked.The y-axis is labelled, paper in millions of tons, and the quantities 4, 9, and 11 are marked.Points Y(14, 9) , W(16, 9) , (19, 4) , and an unnamed point (14, 11) are plotted on the graph, and joined to the respective axes using dotted lines.A concave curve is drawn from the y-axis to the x-axis, passing through the unnamed point (14, 11) , and points W(16, 9) , and X(19, 4) .Point Y is between the curve and the axes.
-Refer to Figure 2.5. If this economy is currently considering switching from point X to point W, what is the opportunity cost of each newly produced ton of paper?
Definitions:
Classical Conditioning
A learning process in psychology where two stimuli are repeatedly paired together until an individual associates them with each other, leading to a change in behavior.
CS
An abbreviation often used in psychology and neuroscience for "Conditioned Stimulus," a component of classical conditioning.
US
In the context of classical conditioning, it stands for the Unconditioned Stimulus, which automatically triggers a response without any learning needed.
Conditioned Stimulus
A formerly neutral cue that, after being linked with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to evoke a conditioned response over time.
Q14: The process of formalizing acceptance of the
Q16: Which of the following terms describes a
Q20: On a diagram of a production possibility
Q22: How might you approach the prioritization of
Q62: Refer to Figure 2.2.Suppose Atikamekw Cree are
Q65: Which of the following statements is true
Q98: Refer to Figure 2.6.In response to changing
Q141: An example of a factor of production
Q210: If a demand curve shifts to the
Q300: If consumers believe the price of hybrid