Scenario 9-2
• For a small country called Boxland,the equation of the domestic demand curve for
cardboard is  ,
,
where 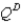 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded,in tons,and
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard demanded,in tons,and 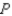 represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
• For Boxland,the equation of the domestic supply curve for cardboard is 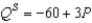 ,
,
where 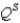 represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied,in tons,and
represents the domestic quantity of cardboard supplied,in tons,and 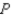 again
again
represents the price of a ton of cardboard.
-Refer to Scenario 9-2.Suppose the world price of cardboard is $60.Then,relative to the no-trade situation,international trade in cardboard
Definitions:
Behaving
Acting in a manner according to certain standards, rules, or expectations in social contexts.
Heteronomous Morality
The first stage of moral development in Piaget’s theory, occurring from 4 to 7 years of age. Justice and rules are conceived of as unchangeable properties of the world, beyond the control of people.
Immanent Justice
The belief, often held by children, that moral behavior is immediately rewarded and immoral behavior is immediately punished.
Autonomous Morality
The second stage of moral development in Piaget’s theory, displayed by older children (about 10 years of age and older). The child becomes aware that rules and laws are created by people and that, in judging an action, one should consider the actor’s intentions as well as the consequences.
Q20: Refer to Figure 9-2.The world price for
Q56: Refer to Figure 9-9.Total surplus in this
Q69: Using demand and supply diagrams,show the difference
Q72: When a country allows international trade and
Q115: Refer to Figure 9-6.The amount of revenue
Q146: When externalities exist,buyers and sellers<br>A) neglect the
Q260: Refer to Figure 10-13.If 250 units of
Q261: Refer to Figure 10-10.Which of the following
Q368: Refer to Figure 10-12.An alternative label for
Q388: In the case of a technology spillover,the