Figure 24-6.On the left-hand graph,MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money; on the right-hand graph,AD represents aggregate demand.The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs.
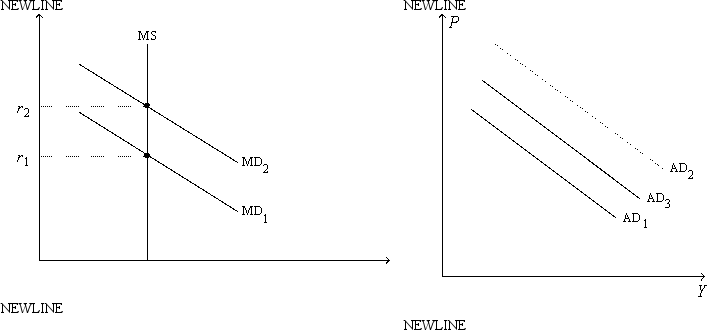
-Refer to Figure 24-6.Suppose the multiplier is 5 and the government increases its purchases by $10 billion.Also,suppose the AD curve would shift from AD1 to AD2 if there were no crowding out; the AD curve actually shifts from AD1 to AD3 with crowding out.Also,suppose the horizontal distance between the curves AD1 and AD3 is $20 billion.The extent of crowding out,for any particular level of the price level,is
Definitions:
Q
Quantity, frequently used in economic equations and discussions to denote the amount of goods produced or consumed.
PQ
The product of price (P) and quantity (Q), often used in economics to calculate total revenue or expenditure.
P
Typically refers to "Price" in economic models, representing the monetary value assigned to a good or service in the market.
V
Typically stands for Velocity in economic contexts, referring to the rate at which money circulates in the economy.
Q60: Markets in which funds are transferred from
Q76: During a recession,output declines resulting in<br>A)lower unemployment
Q77: An example of the problem of _
Q81: Which of the following benefit directly from
Q82: If there are four goods in a
Q135: Refer to Figure 24-2.If the money-supply curve
Q165: Refer to Figure 23-1.If the economy starts
Q334: In the long run,the level of output<br>A)
Q340: If the multiplier is 5,then the MPC
Q371: Refer to Figure 23-2.The appearance of the