Suppose a monopolist faces the demand curve and cost curves shown below. 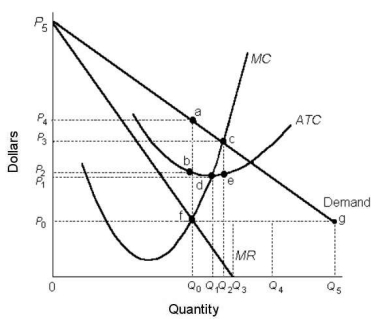 FIGURE 10-5
FIGURE 10-5
-Refer to Figure 10-5.The average per unit profit earned by this profit-maximizing single-price monopolist is
Definitions:
Variable Costing
This accounting method includes only variable costs - costs that vary with production level - in the calculation of the cost of goods sold.
Unit Product Cost
The total cost associated with creating one unit of product, including materials, labor, and overhead.
Variable Costing
An accounting method where only the variable production costs are allocated to the product, while fixed costs are treated as period costs.
Net Operating Income
The total income from operations of a company before taxes and interest deductions.
Q22: Refer to Table 7-4.Average fixed costs for
Q34: The theory of equal net advantage is
Q72: Refer to Table 9-1.Suppose this firm is
Q86: The difference between temporary factor-price differentials and
Q101: Consider a perfectly competitive industry in the
Q108: Why will a perfectly competitive firm not
Q113: An allowable defence for a merger according
Q120: The supply curve for a perfectly competitive
Q139: The market demand curve for a perfectly
Q152: Suppose a perfectly competitive firm is producing