The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. 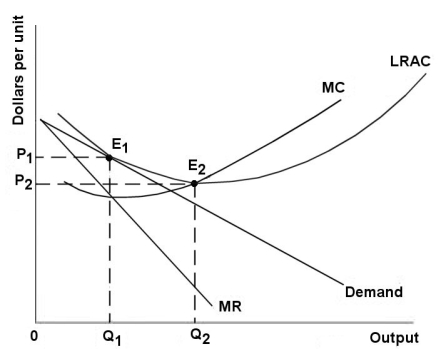 FIGURE 11-3
FIGURE 11-3
-Refer to Figure 11-3.In the long run,a monopolistically competitive firm will
Definitions:
Phosphate Groups
Phosphate groups are chemical groups consisting of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms (PO4), important in energy transfer within cells.
Ribose Groups
Components of RNA molecules consisting of five-carbon sugars connected to the nucleobases and phosphate groups.
Polysaccharide
A complex carbohydrate composed of a long chain of monosaccharide units bonded together, serving various functions including energy storage and structural roles.
Nucleotide
A molecule consisting of one or more phosphate groups, a 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine).
Q3: Suppose that a single-price monopolist knows the
Q4: Refer to Table 13-1.How many units of
Q27: Suppose a firm producing aircraft engines is
Q43: Suppose a firm is using 100 units
Q66: In general,a profit-maximizing firm will purchase a
Q77: Refer to Table 9-1.Suppose this firm is
Q79: According to economist George Stigler,the process of
Q83: Natural barriers to firms to entering an
Q87: Consider two firms,A and B,that are producing
Q124: Suppose capital costs $280 per unit and