Let U(x,y) = 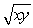 with MUx =
with MUx = 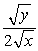 and MUy =
and MUy = 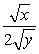 .Let I = $100,Px = $10 and Py = $10 be the initial set of prices and income.Now,let Px rise to $25.What are the (approximate) substitution and income effects of this change in prices?
.Let I = $100,Px = $10 and Py = $10 be the initial set of prices and income.Now,let Px rise to $25.What are the (approximate) substitution and income effects of this change in prices?
Definitions:
Substitution Effect
The change in the consumption of goods in response to a change in their relative prices, holding the consumer's level of utility constant.
Labor Supply Curve
The graphical representation showing the relationship between the different wage rates and the quantity of labor that workers are willing to supply.
Wage Rate
The amount of compensation a worker receives per unit of time, such as an hour or a week, for their labor.
Backward Bending
A curve, often related to the labor supply, indicating that beyond a certain wage level, as wages increase, individuals may choose to work fewer hours, prioritizing leisure over additional income.
Q1: Suppose a $1 tax is levied on
Q8: Which of the following statement is false?
Q22: Consider the utility function U = 5x
Q24: You own a small bookstore.You have hired
Q38: An indivisible input is<br>A) an input that
Q38: A graph that plots the consumer's level
Q43: A measure of monopoly power,the percentage markup
Q46: In a perfectly competitive market,which of the
Q56: Identify the truthfulness of the following statements.
Q56: Let a firm's long run total cost