A light ray goes through two thick rectangular slabs of glass,each of the same uniform thickness.The first slab has index of refraction n1 and the second n2.If n1 < n2.How does the original angle of incidence i into the first slab compare to the final angle of refraction f where the ray leaves the second slab going back into air? 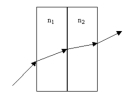
Definitions:
Cellular Network
A communication network where the last link is wireless, often used for mobile phone communication, it's structured into cells, each served by a fixed-location transceiver.
Internet Access
The ability of individuals and organizations to connect to the Internet using computer terminals, computers, and other devices; and to access services such as email and the World Wide Web.
Network Access
The ability or permission to use a network for sending or receiving data.
Wireless Signal
Electromagnetic waves used to communicate between devices without the need for physical wires or cables, utilized in technologies such as Wi-Fi and cellular data.
Q3: It is desired to use an electron
Q15: A 2.5 cm-long horizontal wire segment has
Q27: What minimum thickness of oil (n =
Q37: When the voltage across a resistor is
Q37: In a laboratory experiment,you are given
Q43: The sun radiates at a power
Q48: In a camera,the image focused on the
Q49: Two lenses,the first with focal length 10.0
Q60: 1 THz = ?<br>A) 10<sup>3</sup> Hz<br>B) 10<sup>6</sup>
Q70: A thin lens of focal length -12.5