Refer to the MegaStat/Excel output for the Wilcoxon signed ranks test given in the table below. 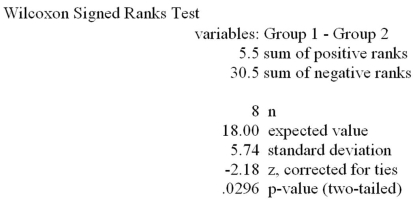
At a significance level of .01,which one of the following rejection point conditions is correct regarding the null hypothesis H0: D1 and D2 are identical probability distributions and the alternative hypothesis of Ha: D1 is shifted to the left of D2.
Definitions:
Q2: A transferable emission permit scheme will always
Q19: Define the three different types of equity
Q32: Cyclical variation exists when the magnitude of
Q34: The sign test is a nonparametric test
Q36: Based on the following data,a forecaster used
Q42: A unit that fails to meet specifications
Q50: A tire manufacturer needs to make a
Q98: When employing measurement data to study
Q128: Given the following data,compute the mean absolute
Q138: In the quadratic regression model