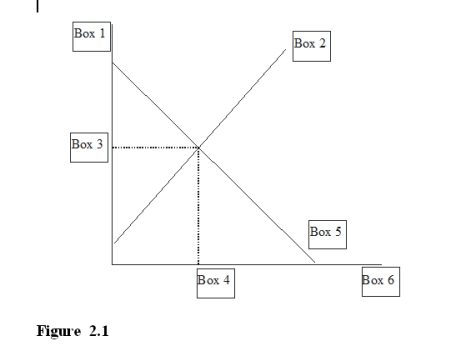
-In Figure 2.1, a "Q*" for equilibrium quantity would go in
Definitions:
P-value
The P-value is a statistical parameter that helps to determine the significance of the results from a hypothesis test, indicating the probability of observing the results if the null hypothesis is true.
P-value
A statistic that measures the probability of obtaining an observed result, or more extreme, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true.
Null Hypothesis
A statement in statistics that proposes there is no significant difference or effect, and any observed difference is due to sampling or experimental error.
Hypothesis Testing
A statistical method used to determine whether there is enough evidence in a sample of data to infer that a certain condition holds for the entire population.
Q33: The correct formula for sodium tetracyanonickelate(II) ion
Q50: Of the collection of supply and demand
Q51: If goods A and B are considered
Q53: If a firm has two production alternatives
Q61: For a linear and upward sloping supply
Q69: Imagine an economist ordering pizza by the
Q70: Labile complexes are coordination complexes that<br>A) are
Q81: The source of diminishing returns is<br>A)The efficiency
Q83: If the price is less than the
Q187: Of the collection of supply and demand