Samples Corporation manufactures one product. It does not maintain any beginning or ending Work in Process inventories. The company uses a standard cost system in which inventories are recorded at their standard costs and any variances are closed directly to Cost of Goods Sold. There is no variable manufacturing overhead.
The standard cost card for the company's only product is as follows:
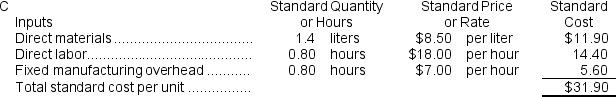 The standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate was based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $140,000 and budgeted activity of 20,000 hours.
The standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate was based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $140,000 and budgeted activity of 20,000 hours.
During the year, the company completed the following transactions:
a. Purchased 49,500 liters of raw material at a price of $8.00 per liter. The materials price variance was $24,750 F.
b. Used 45,820 liters of the raw material to produce 32,800 units of work in process. The materials quantity variance was $850 F.
c. Assigned direct labor costs to work in process. The direct labor workers (who were paid in cash) worked 28,440 hours at an average cost of $17.00 per hour. The direct labor rate variance was $28,440 F. The labor efficiency variance was $39,600 U.
d. Applied fixed overhead to the 32,800 units in work in process inventory using the predetermined overhead rate multiplied by the number of direct labor-hours allowed. Actual fixed overhead costs for the year were $154,700. Of this total, $83,700 related to items such as insurance, utilities, and indirect labor salaries that were all paid in cash and $71,000 related to depreciation of manufacturing equipment. The fixed manufacturing overhead budget variance was $14,700 U. The fixed manufacturing overhead volume variance was $43,680 F.
e. Completed and transferred 32,800 units from work in process to finished goods.
f. Sold (for cash) 32,000 units to customers at a price of $38.20 per unit.
g. Transferred the standard cost associated with the 32,000 units sold from finished goods to cost of goods sold.
h. Paid $133,000 of selling and administrative expenses.
i. Closed all standard cost variances to cost of goods sold.
To answer the following questions, it would be advisable to record transactions a through i in the worksheet below. This worksheet is similar to the worksheets in your text except that it has been split into two parts to fit on the page. PP&E (net) stands for Property, Plant, and Equipment net of depreciation.
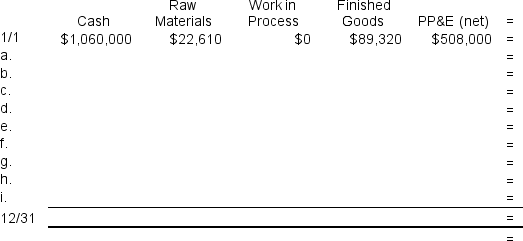
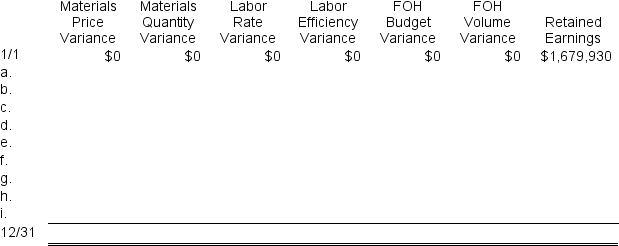
-The net operating income for the year is closest to:
Definitions:
Bank Failures
Occurrences when a bank is unable to meet its obligations to depositors or creditors and ceases operations, often resulting in regulators seizing the institution.
Great Depression
A severe worldwide economic downturn that took place during the 1930s, marked by massive unemployment and widespread poverty.
Lost Confidence
A situation where consumers or investors become pessimistic about the economic prospects, leading to reduced spending and investment.
Prime Interest Rate
The interest rate that commercial banks charge their most credit-worthy customers, often used as a benchmark for various interest rates.
Q10: Manni Products,Inc.,has a Pump Division that manufactures
Q18: When the direct labor cost is recorded,which
Q34: The variable overhead rate variance for July
Q60: The labor efficiency variance for September is:<br>A)
Q66: The fixed overhead volume variance is:<br>A) $43,560
Q137: Buchauer Corporation manufactures one product.It does not
Q139: The fixed manufacturing overhead budget variance for
Q154: The variable overhead efficiency variance for June
Q298: The occupancy expenses in the flexible budget
Q356: The amount shown for net operating income