A family's preferences toward schooling,before and after a fixed-quantity subsidy,are shown in Figure 5-5.Prior to the subsidy,the family is in equilibrium at point J.Assume that public schooling cannot be supplemented with private tutoring. 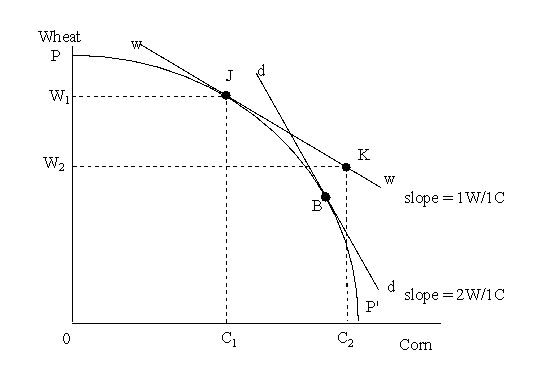
-Refer to Figure 5-5.Public schooling provided in the amount of B0 causes the family to increase consumption of other goods by _____.
Definitions:
Significance Level
The significance level, often denoted as alpha, is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis in a statistical test when it is actually true, representing the risk of a type I error.
Type I Error
The error made when a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected, often referred to as a "false positive."
P Value
The probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the results actually observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true.
Confidence
The degree of certainty or trust in a statistical or experimental result, often expressed as a confidence interval or level.
Q2: A supply curve for a good depicts
Q4: If a production possibility frontier (PPF)is drawn
Q4: The field of organizational behavior relies on
Q14: In the production possibility frontier in Figure
Q20: Which of the following is true of
Q29: Which of the following represents a Cobb-Douglas
Q41: Which of the following is true of
Q65: A farmer is growing corn on an
Q71: When the marginal rates of substitution [MRSs]
Q94: Which of the following does not decline