From the stoichiometry of the reaction 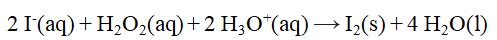 the rate law
the rate law
Definitions:
Eukaryotic Fission
A type of cell division in eukaryotic organisms, similar to binary fission, resulting in the replication and division of a cell into two genetically identical daughter cells.
Proto-Oncogenes
Normal genes that, when mutated, become oncogenes and can contribute to cancer development by promoting cell growth and division.
Checkpoint Genes
Genes that regulate the cell cycle and ensure that each phase is completed accurately before the next one begins, acting as safeguards against cellular damage and uncontrolled cell growth.
Mitosis
The division of a cell resulting in two descendant cells, each inheriting an identical count and form of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical in the growth of regular tissues.
Q5: When 1.00 L of 0.45 M acetic
Q5: Which of the following is a private
Q26: According to a recent survey,which of the
Q35: When was the first period of one-party
Q39: Why is voter turnout typically quite low
Q41: Which level of government is most heavily
Q46: Give an example of an Alkali Metal.
Q54: Calculate the number of moles represented by
Q55: How many atoms are in a 10.0
Q57: In Rutherford's gold foil experiment:<br>A) the alpha