Suppose a single firm has constant marginal cost and faced the demand curve 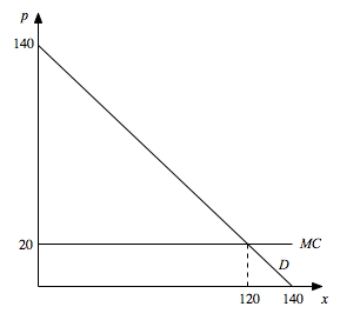
a.Illustrate in this graph how a monopolist who cannot price discriminate would price this good.What is the monopoly price and quantity?
b.Suppose two firms with the same marginal cost as the monopolist operated in this market instead.Suppose quantity is the strategic variable and the two firms simultaneously choose quantity.On a graph with firm 1's output on the horizontal and firm 2's output on the vertical,illustrate firm 2's best response function with numerical labels for each intercept.
c.Add firm 1's best response function and determine the Nash equilibrium quantities.
d.What's the equilibrium price resulting from the quantities you determined in (c)?
e.What would be the equilibrium price if the strategic variable for the firms were price instead?
Definitions:
Absorption Costing
A bookkeeping system that integrates all costs, both direct and indirect, associated with the production of a product into its final cost.
Direct Labor
The wages and salaries paid to employees who are directly involved in the production of goods or the provision of services.
Manufacturing Overhead
Costs in the production process that are not directly tied to a specific product, such as factory utilities or salaries of supervisors.
Product Costs
Expenses directly tied to the production of goods or services, including direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Q3: An increasing returns to scale production function
Q7: When tastes over current and future consumption
Q9: A general partnership,unlike a limited partnership,is an
Q14: In perfectly competitive markets with identical firms,the
Q17: There are no quasilinear tastes that have
Q17: If firms differ in terms of their
Q22: If producer choice sets are convex and
Q31: In a Bayesian incomplete information game,a "belief"
Q43: Cash and credit management are typically the
Q76: The risk-return tradeoff is seen in many