Carver Lumber sells lumber and general building supplies to building contractors in a medium-sized town in Montana. Data regarding the store's operations follow:
o Sales are budgeted at $350,000 for November, $320,000 for December, and $300,000 for January.
o Collections are expected to be 90% in the month of sale and 10% in the month following the sale.
o The cost of goods sold is 75% of sales.
o The company desires to have an ending merchandise inventory equal to 60% of the following month's cost of goods sold. Payment for merchandise is made in the month following the purchase.
o Other monthly expenses to be paid in cash are $24,700.
o Monthly depreciation is $16,000.
o Ignore taxes.
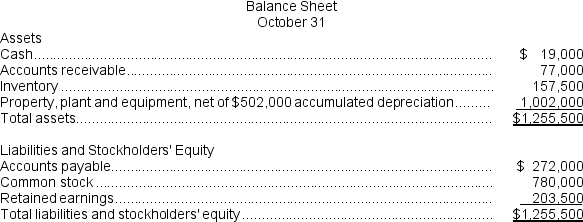
-Retained earnings at the end of December would be:
Definitions:
Pay-for-Knowledge Plans
Compensation strategies that reward employees for acquiring and using specific knowledge or skills that benefit the organization.
Traditional Incentive Systems
Reward structures typically based on performance outcomes, aiming to motivate employees through financial incentives like bonuses, raises, and commissions based on their job performance or targets achieved.
Hourly Workers
Employees who are paid for each hour of work performed, as opposed to receiving a fixed salary.
Free Trade
An economic policy that allows goods and services to be bought and sold across international borders with little or no government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or prohibitions to inhibit their exchange.
Q23: Schlenz Inc., which produces a single product,
Q34: The desired ending inventory of Jurislon for
Q46: The estimated direct labor cost for November
Q130: Lanciotti Corporation manufactures one product.It does not
Q141: A properly constructed segmented income statement in
Q159: Hargett Incorporated makes a single product--an electrical
Q180: Northern Pacific Fixtures Corporation sells a single
Q233: If 54,480 pounds of raw materials are
Q273: Segmented statements for internal use should not
Q289: The unit product cost under absorption costing