Harnett Corporation has two manufacturing departments--Molding and Assembly.The company used the following data at the beginning of the period to calculate predetermined overhead rates: 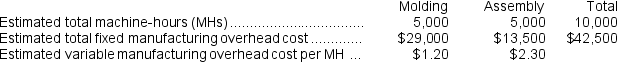 During the period, the company started and completed two jobs--Job E and Job M.Data concerning those two jobs follow:
During the period, the company started and completed two jobs--Job E and Job M.Data concerning those two jobs follow: 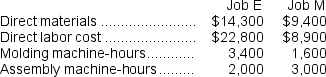 Required:
Required:
a.Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours.Calculate that overhead rate.
b.Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours.Calculate the amount of manufacturing overhead applied to Job E.
c.Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours.Calculate the total manufacturing cost assigned to Job E.
d.Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours and uses a markup of 60% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices.Calculate the selling price for Job E.
e.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both departments.What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Molding department?
f.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments.What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Assembly department?
g.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments.How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job E?
h.Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments.Further assume that the company uses a markup of 60% on manufacturing cost to establish selling prices.Calculate the selling price for Job E.
Definitions:
Credit Period
The amount of time allowed by a seller to a buyer to pay for the goods or services purchased on credit, usually described in days.
Highly Perishable
Describes goods or products that have a short shelf life and require immediate consumption, sale, or processing to avoid spoilage or loss of value.
High Cost Item
Products or services that require a significant amount of money to purchase or maintain, often reflecting quality or luxury status.
Competition
The rivalry between businesses or sellers in the same market, aiming to achieve higher sales, profits, and market share.
Q20: One advantage of the within-subjects approach is
Q68: The journal entry to record the allocation
Q93: The journal entry to record the requisition
Q99: Parlavecchio Corporation's relevant range of activity is
Q125: What is the total of the direct
Q126: The alpha level directly affects the power
Q130: In making the decision to buy the
Q142: Experimental and observational strategies can be used
Q197: If 5,000 units are sold, the variable
Q225: Alberta Corporation uses a job-order costing system.The