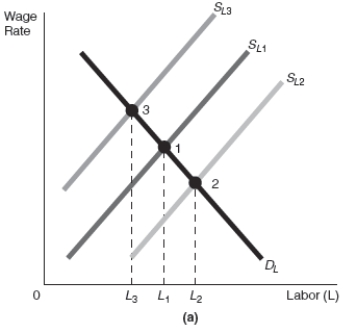
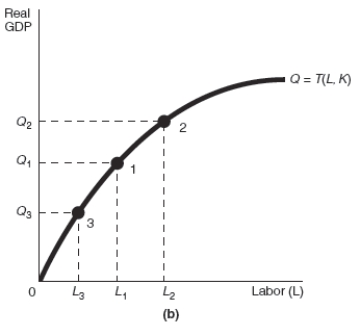
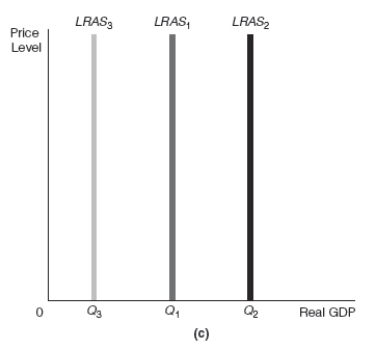
-Refer to Exhibit 17-4 Assume that the starting point in graphs (a) and (b) in Exhibit 17-4 is point 1.After a decrease in income taxes,there would be a ______________________ which would cause a movement along the production function from point 1 to point ______________.The result would be a shift of the LRAS curve from LRAS1 to _______________ resulting in _______________..
Definitions:
Pragnanz
A principle of Gestalt psychology suggesting that individuals will perceive and interpret complex images in the simplest form possible.
Figure-Ground Reversal
A visual perception phenomenon where the viewer can shift perspective to see either the foreground or the background as the dominant aspect.
Top-Down Processing
This is the psychological process where perceptions start with a general overview before moving to specific details.
Detecting Edges
The process involved in identifying the boundaries or changes in brightness in a visual image, crucial for image processing and analysis.
Q6: Refer to Exhibit 34-1.Considering the data,which of
Q24: If a U.S.company operates within a competitive
Q36: To an economist,it is preferable to<br>A) assume
Q66: In the production function Real GDP =
Q71: Refer to Exhibit 34-4.The opportunity cost of
Q79: When income tax rates rise,tax revenues always
Q80: "Absolute real economic growth" is defined as
Q96: Grown children fawning over an elderly parent
Q116: Based upon the equation of exchange,which of
Q126: Public choice deals with<br>A) negative and positive