The fluorocarbon 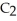
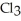
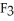 Has a normal boiling point of 47.6 °C.The specific heats of
Has a normal boiling point of 47.6 °C.The specific heats of 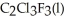 And
And 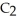
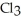
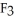 (g) are 0.91 J g-1 °C-1 and 0.67 J g-1 °C-1,respectively.The heat of vaporization of the compound is 27.49 kJ mol-1.The heat required to convert 50.0 g of the compound from the liquid at
(g) are 0.91 J g-1 °C-1 and 0.67 J g-1 °C-1,respectively.The heat of vaporization of the compound is 27.49 kJ mol-1.The heat required to convert 50.0 g of the compound from the liquid at 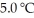 To the gas at 80.0 °C is ________ kJ.
To the gas at 80.0 °C is ________ kJ.
Definitions:
NSAID Medications
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs that are used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain and fever.
Severe Allergy
A critical immune system reaction to a particular allergen that can result in life-threatening symptoms.
Power Influence
The capacity to affect the behavior, decisions, or thinking of others through authority, persuasion, or manipulation.
Objectives
Specific, measurable goals that are designed to achieve an overall aim or target.
Q9: Based on the figure above,the boiling point
Q25: Three types of holes of the cubic
Q27: List the following acids in order of
Q36: A chemical bond for which one of
Q40: Which has the smallest dipole-dipole forces?<br>A)CH<sub>3</sub>Cl<sub> </sub><br>B)HBr<sub>
Q55: Which of the following are Br∅nsted-Lowry acids?<br>I.CH<sub>3</sub>COOH<br>II.[Cu(H<sub>2</sub>O)<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2+
Q72: Arrange the following elements in order of
Q84: A handbook states that to prepare a
Q86: The phenomenon of supercooling refers to the
Q100: Predict the freezing point of a solution