As this graph shows,photosynthesizing eukaryotes have several pigments and accessory pigments that selectively capture the green wavelengths of photons for photosynthesis. 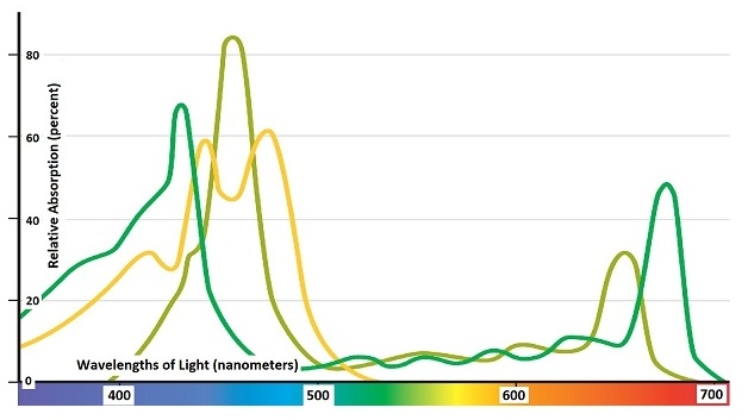
Definitions:
Behaviourism
A psychological approach to understanding abnormal behaviour devised by John B. Watson (1858–1935), which declared that psychology must be restricted to the study of observable features, that is, the behaviour of organisms. Watson considered abnormal functioning to be learned and so believed it could be unlearned. His model for learning was derived from Ivan Pavlov’s (1849–1936) studies of classical conditioning.
Classical Conditioning
A learning process where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a meaningful stimulus and acquires the capacity to elicit similar responses.
Watson
John B. Watson, an American psychologist who established the psychological school of behaviorism.
Early Behaviourists
Psychologists or researchers in the early 20th century who focused on observable behaviors rather than internal processes, founding behaviorism.
Q12: Many studies of potentially useful new drugs
Q12: Mendel kept detailed records of the genetic
Q19: The sodium-potassium pump catalyzes<br>A) equilibrium.<br>B) facilitated diffusion.<br>C)
Q26: Life on Earth is often described as
Q32: The group of organic molecule polymers with
Q41: The small unit of self-replicating DNA used
Q58: A karyotype is produced by inducing cells
Q66: The function of the nucleolus is<br>A) protein
Q72: You are studying genes in yeast and
Q80: In biology lab,your class counts the number