The following is a summary of the steps found in the metabolic pathway known as the Citric Acid Cycle.
Step 1: 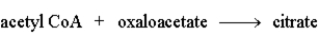 Step 2:
Step 2:  Step 3:
Step 3: 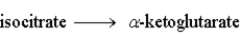 Step 4:
Step 4: 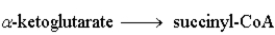 Step 5:
Step 5:  Step 6:
Step 6:  Step 7:
Step 7:  Step 8:
Step 8: 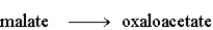 Fill in the blanks in the following question with the appropriate term from the list below.
Fill in the blanks in the following question with the appropriate term from the list below.
oxaloacetate oxidation
citrate reduction
isocitrate consumes
a-ketoglutarate produces
succinyl-CoA NADH
succinate FAD
fumarate NADPH
malate
-Step 6 converts the -CH2-CH2- of succinate to the -CH=CH- of fumarate. This reaction would be classified as a(n) ______________________ reaction.
Definitions:
Alternative Hypotheses
A statement in hypothesis testing that is accepted if the evidence suggests that the null hypothesis is false.
Null Hypothesis
The default position that there is no association between two measured phenomena, or no difference among groups being compared.
P-Value
The probability of observing test results at least as extreme as the results actually observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true.
Critical Value
A threshold in hypothesis testing that defines the boundary or cutoff point at which the test statistic is considered significant.
Q1: Which of the following is a secondary
Q5: Structure _ would exist as a positive
Q22: Human DNA consists of 44 autosomal chromosomes
Q36: Which of the following pass through both
Q39: _is the type of force present between
Q47: Which of the following substances can react
Q56: If you absorb 0.0056 rad of energy
Q62: When the following equation is balanced using
Q63: ATP plays a role in all of
Q69: This substance is water-soluble. A solution of