You have $5 to spend on any combination of goods A and
A.The utility maximizing combination here is to buy 1 of A and 3 of
B.Are you maximizing your utility? If so,explain why.If not,what combination of goods should you buy?
(a)The completed table:
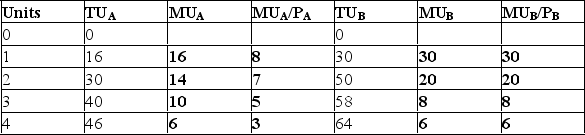
(b)If you purchase 2 of A and 1 of B you are not maximizing your utility.To see why not,use the utility maximizing rule.For good A compute MUA/PA = 7 and for good B compute MUB/PB = 30.Since MUB/PB > MUA/PA you are not at a utility maximizing combination of goods;you should reallocate your $5 and buy more B and less
B.The price of good A is $2 and the price of good B is $1.You have calculated the following utility values for yourself:
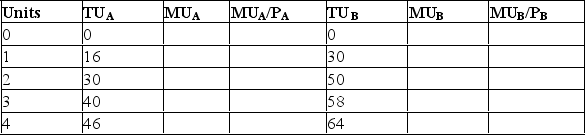
(a)Fill in the empty columns of the table.
(b)You have purchased 2 units of good A and 1 unit of good
B.With this latter combination we see that MUA/PA = 8 = MUB/PB and we have satisfied the utility maximizing rule.
Definitions:
Competent Practitioners
Individuals who possess the required skills, knowledge, and ability to perform their professional duties effectively.
Medicalized
The process by which human conditions and problems come to be defined and treated as medical issues, often involving interventions by health professionals.
Professionalization
The process of becoming a professional; acquiring the skills, knowledge, and standards needed for a profession, often involving formal education and training.
Professionalization of Medicine
The process by which the practice and study of medicine have become increasingly structured and formally recognized as a profession, with specific training, ethical, and standards criteria.
Q37: All of the following,except one,would cause an
Q44: Refer to the information above to answer
Q50: What is significant about the level of
Q56: Suppose it takes 30 workers and 120
Q58: Refer to the information above to answer
Q65: The data in Table 6.1 are for
Q65: Refer to the above graph to answer
Q91: Which of the following statements about diseconomies
Q136: Refer to the information above to answer
Q170: Which of the following statements is true