For the reaction CuS(s)+ H2(g) 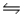
H2S(g)+ Cu(s),
G°f (CuS)= -53.6 kJ/mol
G°f (H2S)= -33.6 kJ/mol
H°f (CuS)= -53.1 kJ/mol
H°f (H2S)= -20.6 kJ/mol
Calculate G at 798 K and 1 atm pressure (assume S° and H° do not change with temperature).
Definitions:
Electrocardiograph Monitor
A device used to record the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time, detecting cardiac abnormalities.
Renal Dialysis
A medical procedure that artificially removes waste products and excess fluid from the blood when the kidneys are unable to perform their natural function.
Potassium Wasting
A condition where the body excretes an excessive amount of potassium, leading to low levels of potassium in the blood.
Gastroenteritis
An inflammation of the stomach and intestines, usually resulting from bacterial toxins or viral infection and causing vomiting and diarrhea.
Q2: Which one of these metals would normally
Q13: What is the pH at the equivalence
Q16: At 340 K, K<sub>p</sub> = 69 for
Q27: Aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)<sub>3</sub>, is<br>A)an acid.<br>B)an amphoteric hydroxide.<br>C)a
Q31: The isotope of iodine with mass number
Q37: A titration of an acid and base
Q40: At 1500°C the equilibrium constant for
Q83: The half-cell reaction for the oxidation
Q131: Determine how much energy is released when
Q148: Complete and balance the following redox