For the reaction CuS(s)+ H2(g) 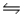
H2S(g)+ Cu(s),
G°f (CuS)= -53.6 kJ/mol
G°f (H2S)= -33.6 kJ/mol
H°f (CuS)= -53.1 kJ/mol
H°f (H2S)= -20.6 kJ/mol
Calculate G at 798 K and 1 atm pressure (assume S° and H° do not change with temperature).
Definitions:
Tax Return
A tax return is a form filed with a tax authority that reports income, expenses, and other pertinent tax information. Taxes owed or a refund owed to the taxpayer are determined through this form.
Roofer
A professional who specializes in the construction, repair, and installation of roofs.
Nontaxable Income
Income that is not subject to income tax at the federal, state, or local level.
Alimony Payment
A financial support that one ex-spouse is legally obligated to provide to the other during or after the process of legal separation or divorce.
Q12: Calculate the concentration of oxalate ion (C<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>)in
Q17: Potassium superoxide, KO<sub>2</sub>(s), is used in the
Q17: Complete and balance the nuclear equation <img
Q18: In n-type semiconductors<br>A)the energy gap between the
Q41: Identify the conjugate base of HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup><br>A)H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub><br>B)CO<sub>3</sub><sup>2-</sup><br>C)OH<sup>-</sup><br>D)CO<sub>2</sub><br>E)CO
Q56: What effect does increasing temperature have on
Q63: Which one of these elements would give
Q74: Determine the cell diagram for the
Q104: The following reaction is nonspontaneous at
Q137: Under standard-state conditions, which of the