Consider the reaction CO(g)+ 2H2(g) 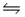
CH3OH(l)at 25°C.
G°f (CO)= -137.3 kJ/mol
G°f (CH3OH)= -166.3 kJ/mol
H°f (CO)= -110.5 kJ/mol
H°f (CH3OH)= -238.7 kJ/mol
S°(CO)= 197.9 J/K·mol
S°(CH3OH)= 126.8 J/K·mol
Calculate G° at 25°C.
Definitions:
Supplemental Medical Coverage
Additional health insurance that covers costs not covered by a primary insurance plan, including copayments, deductibles, and non-covered services.
Market Pricing
The process of determining the value of a job in the external job market by comparing it with similar jobs in other organizations.
Equity
Fair treatment and distribution of resources, or in finance, the value of an ownership interest in property, including shareholders' equity in a corporation.
Efficiency
The ability to achieve maximum productivity with minimum wasted effort or expense.
Q2: What is the pH of a 0.014
Q12: Ozone (O<sub>3</sub>)in the atmosphere can reaction
Q12: Consider an electrochemical cell constructed from the
Q22: If the pH of seawater is 8.0,
Q41: Identify the conjugate base of HCO<sub>3</sub><sup>-</sup><br>A)H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub><br>B)CO<sub>3</sub><sup>2-</sup><br>C)OH<sup>-</sup><br>D)CO<sub>2</sub><br>E)CO
Q66: Complete and balance the following redox
Q79: Calculate the molar solubility of AgBr in
Q80: Given the following K<sub>a</sub> values, which anion
Q87: For the electrochemical cell Ni(s)| Ni<sup>2+</sup>(1 M)||
Q110: A balanced nuclear equation representing the alpha